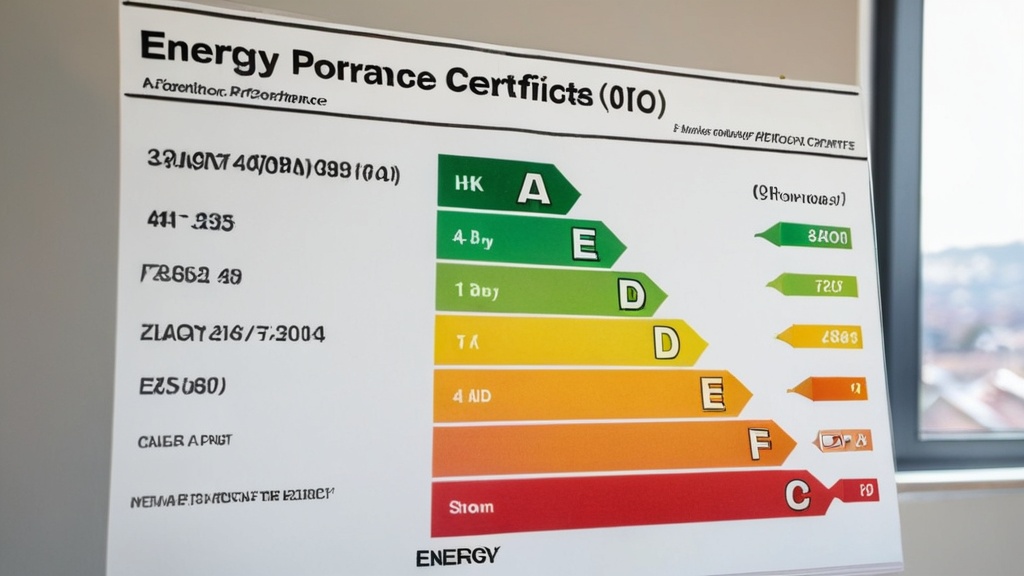
An Energy Performance Certificate (EPC) serves as a vital tool in assessing the energy efficiency of a property. This document provides potential buyers and tenants with an overview of how energy-efficient a building is, represented through a rating system that ranges from A to G. A rating of A indicates the highest level of energy efficiency, while G signifies the lowest.
The EPC not only highlights the current energy performance but also offers recommendations for improvements, making it an essential resource for anyone considering a property. EPCs became a requirement in many countries as part of efforts to promote energy conservation and reduce carbon emissions. They aim to inform consumers about the energy consumption of a property, allowing them to make informed decisions.
Understanding the EPC can empower us to take steps toward more sustainable living.
Key Takeaways
- An Energy Performance Certificate (EPC) assesses a property’s energy efficiency and environmental impact.
- EPC ratings are calculated based on factors like insulation, heating systems, and energy consumption.
- Higher EPC ratings indicate better energy efficiency, leading to lower energy bills and increased property value.
- Landlords and homeowners must comply with EPC requirements to meet legal standards and improve sustainability.
- EPC recommendations provide practical steps to enhance energy performance and reduce carbon emissions.
How is an EPC calculated?
Calculating an EPC involves a comprehensive assessment of various factors related to a property’s energy use. Energy assessors evaluate the building’s structure, heating systems, insulation, and other elements that contribute to its overall energy performance. The assessment process typically includes on-site inspections and the use of specialized software that analyzes the data collected.
This software applies standardized methodologies to determine the energy efficiency rating. The calculation considers several aspects, including the type of heating system, the age of the property, and the materials used in construction. Each element contributes to the overall energy consumption and efficiency of the building.
After gathering all necessary information, the assessor inputs it into the software, which generates the EPC rating based on established benchmarks. This systematic approach ensures that each property is evaluated fairly and consistently.
The importance of EPC ratings

EPC ratings hold considerable importance for both property owners and prospective buyers or tenants. For homeowners, a higher EPC rating can lead to reduced energy bills and increased comfort within the living space. Properties with better energy efficiency often attract more interest in the real estate market, as buyers increasingly prioritize sustainability.
A favorable EPC rating can enhance a property’s marketability and potentially increase its value. For tenants, understanding EPC ratings can guide decisions about where to live. A property with a high rating indicates lower energy costs and a reduced environmental impact.
As awareness of climate change grows, many individuals seek homes that align with their values regarding sustainability. EPC ratings provide a clear and accessible way for us to evaluate a property’s energy performance, making them an essential consideration in today’s housing market.
What factors affect EPC ratings?
Several factors influence EPC ratings, each contributing to a property’s overall energy efficiency. The type of heating system installed plays a significant role; modern, efficient systems tend to yield better ratings than older models. Insulation quality is another critical factor; well-insulated properties retain heat more effectively, reducing energy consumption during colder months.
The size and layout of a property can also impact its EPC rating. Larger homes may require more energy to heat or cool, while properties with open floor plans may benefit from improved airflow and natural light. Additionally, the presence of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, can positively affect a property’s rating by reducing reliance on traditional energy sources.
Understanding these factors allows us to identify areas for improvement and work towards achieving better energy performance.
How to improve your EPC rating
| Metric | Description | Typical Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency Rating | Measures the energy efficiency of a building on a scale from A (most efficient) to G (least efficient) | A to G | High – Indicates potential energy savings and environmental impact |
| Estimated Energy Consumption | Annual energy use of the property measured in kWh per square meter | 50 – 400 kWh/m²/year | Medium – Helps estimate running costs and energy demand |
| CO2 Emissions | Annual carbon dioxide emissions associated with the property’s energy use, measured in kg/m²/year | 5 – 50 kg/m²/year | High – Reflects environmental impact and sustainability |
| Potential Energy Efficiency Rating | Shows the possible rating after recommended improvements are made | A to G | High – Indicates scope for energy performance improvement |
| Recommended Improvements | List of suggested measures to improve energy efficiency (e.g., insulation, double glazing) | Varies by property | High – Guides owners on how to reduce energy use and costs |
| Validity Period | Duration for which the EPC is valid before a new assessment is required | 10 years | Medium – Ensures up-to-date energy performance information |
Improving an EPC rating involves implementing various strategies aimed at enhancing energy efficiency within a property. One effective approach is upgrading insulation in walls, roofs, and floors. Proper insulation minimizes heat loss during winter months and keeps homes cooler in summer, leading to reduced energy consumption.
Investing in modern heating systems can also yield significant improvements in EPC ratings. High-efficiency boilers or heat pumps consume less energy while providing adequate heating. Additionally, installing double or triple-glazed windows can help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures by reducing drafts and heat loss.
Simple changes like switching to LED lighting can further contribute to lower energy bills and improved ratings.
EPC requirements for landlords and homeowners
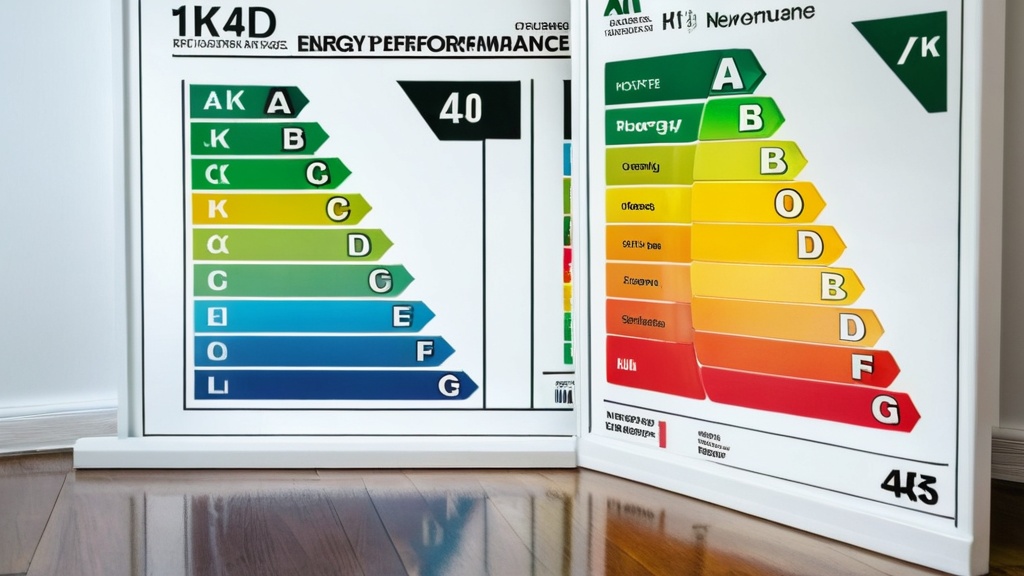

Landlords and homeowners must adhere to specific EPC requirements to comply with regulations in many regions. For landlords, obtaining an EPC is mandatory before renting out a property. The certificate must be made available to potential tenants at the time of viewing, ensuring they have access to essential information about the property’s energy performance.
Homeowners looking to sell their properties must also provide an EPC to prospective buyers. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in penalties or fines. Understanding these requirements is crucial for both landlords and homeowners, as it ensures compliance with local laws while promoting transparency in the real estate market.
The role of EPCs in reducing carbon emissions
EPCs play a vital role in efforts to reduce carbon emissions associated with residential properties. By providing clear information about energy efficiency, these certificates encourage property owners to make informed decisions regarding upgrades and improvements. As more individuals invest in enhancing their properties’ energy performance, overall energy consumption decreases, leading to lower carbon emissions.
Governments and organizations recognize the importance of EPCs in achieving sustainability goals. Initiatives aimed at improving building standards often rely on EPC data to track progress and identify areas needing attention. As we collectively strive for a greener future, understanding the role of EPCs becomes increasingly important in shaping policies and practices that promote environmental responsibility.
Understanding the EPC recommendations
EPCs include recommendations for improving a property’s energy efficiency, offering valuable insights for homeowners and landlords alike. These suggestions often focus on cost-effective measures that can lead to significant improvements in energy performance without requiring substantial investments. Common recommendations may include upgrading insulation, installing more efficient heating systems, or incorporating renewable energy sources.
Understanding these recommendations empowers us to take actionable steps toward enhancing our properties’ energy efficiency. Implementing even a few suggested changes can lead to noticeable improvements in both comfort and cost savings over time. As we consider our options for upgrading our homes or rental properties, referring to the EPC recommendations can guide us toward making informed decisions that benefit both our wallets and the environment.
Energy Performance Certificates (EPCs) are essential for understanding the energy efficiency of a property, but there are many ways to improve energy usage in daily life. For instance, if you’re looking to save energy while cooking, you might find useful tips in this article on how to save energy while cooking. Implementing these strategies can not only reduce your energy bills but also contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle.
FAQs
What is an Energy Performance Certificate (EPC)?
An Energy Performance Certificate (EPC) is an official document that provides information about the energy efficiency of a building. It rates the property on a scale from A (most efficient) to G (least efficient) and includes recommendations for improving energy efficiency.
Who needs an Energy Performance Certificate?
An EPC is required when a property is built, sold, or rented out. It is mandatory in many countries to provide an EPC to potential buyers or tenants to inform them about the energy performance of the property.
How is the energy efficiency rating determined?
The energy efficiency rating is calculated based on factors such as the building’s insulation, heating systems, windows, and overall energy consumption. A qualified assessor conducts an inspection and uses standardized software to generate the rating.
How long is an Energy Performance Certificate valid?
An EPC is typically valid for 10 years from the date of issue. After this period, a new assessment must be carried out if the property is sold or rented again.
What information does an EPC include?
An EPC includes the energy efficiency rating, environmental impact rating, estimated energy costs, and recommendations for improving the building’s energy performance. It also provides details about the property and the assessor.
Can an EPC help reduce energy bills?
Yes, by following the recommendations on an EPC, property owners can improve energy efficiency, which can lead to lower energy consumption and reduced energy bills.
Is an EPC required for commercial properties?
Yes, commercial properties also require an EPC when they are constructed, sold, or leased. The requirements may vary depending on the country or region.
Who can issue an Energy Performance Certificate?
EPCs must be issued by accredited and qualified energy assessors who have undergone specific training and certification to carry out energy assessments.
What happens if a property does not have an EPC when required?
Failing to provide an EPC when required can result in legal penalties, fines, or delays in property transactions. It is important to ensure an EPC is obtained and available during the sale or rental process.
Are there any exemptions from needing an EPC?
Certain properties may be exempt from requiring an EPC, such as places of worship, temporary buildings, or buildings scheduled for demolition. Exemptions vary by jurisdiction and should be verified with local regulations.